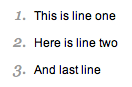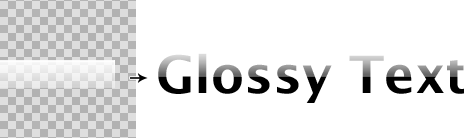Earlier before I have written an article about current best CSS hacks which you can see here And now here's the list of today's most used CSS tricks and tips. I have added image examples for most of them because of critics on CSS hacks article. If you think I have missed any please let me know
1. Rounded corners without images
<b class="rtop">
<b class="r1"></b> <b class="r2"></b> <b class="r3"></b>
<b class="r4"></b>
</b>
<!--content goes here -->
<b class="rbottom">
<b class="r4"></b> <b class="r3"></b> <b class="r2"></b>
<b class="r1"></b>
</b>
</div>
.rtop, .rbottom{display:block}
.rtop *, .rbottom *{display: block; height: 1px; overflow: hidden}
.r1{margin: 0 5px}
.r2{margin: 0 3px}
.r3{margin: 0 2px}
.r4{margin: 0 1px; height: 2px}
2. Style your order list
<li>
This is line one
</li>
<li>
Here is line two
</li>
<li>
And last line
</li>
</ol>
ol {
font: italic 1em Georgia, Times, serif;
color: #999999;
}
ol p {
font: normal .8em Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
color: #000000;
}
3. Tableless forms
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input id="name" name="name"><br>
<label for="address">Address</label>
<input id="address" name="address"><br>
<label for="city">City</label>
<input id="city" name="city"><br>
</form>
label,input {
display: block;
width: 150px;
float: left;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
label {
text-align: right;
width: 75px;
padding-right: 20px;
}
br { clear: left; }
4. Double blockquote
background: url(images/open-quote.gif) no-repeat left top;
padding-left: 18px;
font: italic 1.4em Georgia, "Times New Roman", Times, serif;
}
5. Gradient text effect
h1 {
font: bold 330%/100% "Lucida Grande";
position: relative;
color: #464646;
}
h1 span {
background: url(gradient.png) repeat-x;
position: absolute;
display: block;
width: 100%;
height: 31px;
}
<!--[if lt IE 7]>
<style>
h1 span {
background: none;
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.AlphaImageLoader
(src='gradient.png', sizingMethod='scale');
}
</style>
<![endif]-->
6. Vertical centering with line-height
height:100px;
}
div *{
margin:0;
}
div p{
line-height:100px;
}
Content here
7. Rounded corners with images
<div class="roundtop">
<img src="tl.gif" alt=""
width="15" height="15" class="corner"
style="display: none" />
</div>
CONTENT
<div class="roundbottom">
<img src="bl.gif" alt=""
width="15" height="15" class="corner"
style="display: none" />
</div>
</div>
.roundcont {
width: 250px;
background-color: #f90;
color: #fff;
}
.roundcont p {
margin: 0 10px;
}
.roundtop {
background: url(tr.gif) no-repeat top right;
}
.roundbottom {
background: url(br.gif) no-repeat top right;
}
img.corner {
width: 15px;
height: 15px;
border: none;
display: block !important;
}
8. Multiple class name
.class1 { border:2px solid #666; }
.class2 {
padding:2px;
background:#ff0;
}
9. Center horizontally
#container {
margin:0px auto;
}
10. CSS Drop Caps
This paragraph has the class "introduction".
If your browser supports the pseudo-class
"first-letter", the first letter will be
a drop-cap.
p.introduction:first-letter {
font-size : 300%;
font-weight : bold;
float : left;
width : 1em;
}
11. Prevent line breaks in links, oversized content to brake
white-space:nowrap;
}
#main{
overflow:hidden;
}
12. Show firefox scrollbar, remove textarea scrollbar in IE
overflow:-moz-scrollbars-vertical;
}
textarea{
overflow:auto;
}